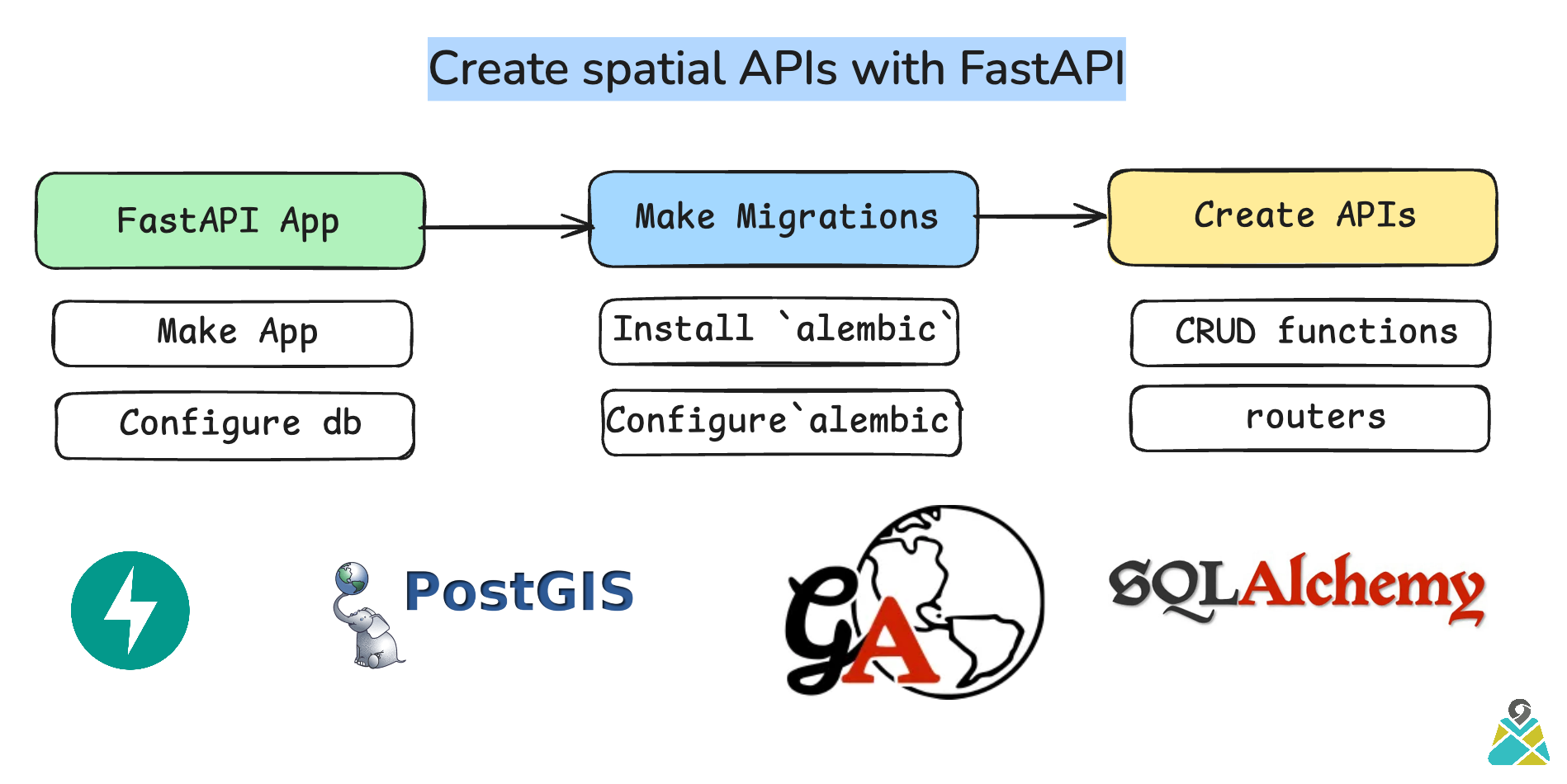
Create spatial APIs with FastAPI
Posted on January 6, 2025
8 minutes
When working with geospatial data in a FastAPI application, one of the most common tasks is to store and retrieve geographical information, such as points, using databases. If you’re working with PostGIS and GeoAlchemy2 , you can efficiently manage and query geospatial data like points.
In this blog post, we’ll walk through how to set up a FastAPI app to retrieve all point-based records stored in a database and return them in an easy-to-use format.
Check GitHub code : https://github.com/Rotten-Grapes-Pvt-Ltd/create-spatial-fastapi
Prerequisites
Before we get started, make sure you have the following set up:
- PostgreSQL with PostGIS extension: This is necessary for storing geospatial data.
- GeoAlchemy2: This library provides integration between SQLAlchemy and PostGIS.
- FastAPI: To build the web application.
- SQLAlchemy: To handle database sessions and queries.
This blog is structured in a way that we explain logic and then code as well
Create FASTAPI app
We’ll start by creating a fastapi app and virtualenv
- Create virtual environment first and activate it
python3 -m venv env
source env/bin/activate- Install packages
pip install "fastapi[standard]" - Make folder structure as following
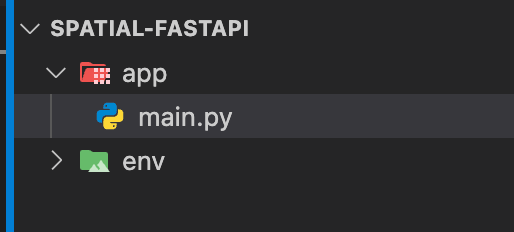
- Write boilerplate code in
main.py
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
def read_root():
return {"Hello": "World"}- run FastAPI code
cd app
uvicorn main:app --reload
Add database settings
- Install packages
pip install sqlalchemy geoalchemy2 pydantic-settings asyncpg greenletNow we’ll add files and connection to database
- Let’s start by creating
.envand adding database url based on following details
username = postgres
password = postgres
host = localhost
port = 5432
db = fastpg
DATABASE_URL=postgresql+asyncpg://postgres:postgres@localhost:5432/fastpg- create
app/config.pyto load.env
from pydantic_settings import BaseSettings
class Settings(BaseSettings):
DATABASE_URL: str
class Config:
env_file = ".env"
case_sensitive = True # Ensure environment variables are case-sensitive
extra = "ignore" # Ignore extra env vars not defined in model
settings = Settings(_env_file=".env") # Pass env file explicitly- create
app/database.py
from sqlalchemy.ext.asyncio import AsyncSession, create_async_engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker, declarative_base
from config import settings
DATABASE_URL = settings.DATABASE_URL
engine = create_async_engine(DATABASE_URL, future=True, echo=True)
SessionLocal = sessionmaker(bind=engine, class_=AsyncSession, expire_on_commit=False)
Base = declarative_base()
async def get_db():
async with SessionLocal() as session:
yield session- create
app/models.py
from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String
from geoalchemy2 import Geometry
from database import Base
class Item(Base):
__tablename__ = "items"
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, index=True)
name = Column(String, index=True)
description = Column(String, nullable=True)
geom = Column(Geometry("POINT"))- create
app/schemas.py
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import Optional
class ItemBase(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Optional[str]
geom: str # WKT (Well-Known Text)
class ItemCreate(ItemBase):
pass
class Item(ItemBase):
id: int
class Config:
from_attributes = True
- Edit
main.pyto get database when app starts running
from fastapi import FastAPI
from contextlib import asynccontextmanager
from database import engine, Base
@asynccontextmanager
async def lifespan(app: FastAPI):
async with engine.begin() as conn:
await conn.run_sync(Base.metadata.create_all)
yield
app = FastAPI(lifespan=lifespan)
@app.get("/")
def read_root():
return {"Hello": "World"}Setup Migrations
Migrations allows us to keep track of database changes
- Setup
alembic
pip install alembic
alembic init migrationsby doing this, new file alembic.ini as well as new folder migrations will be created
- Edit
alembic.iniwith sqlalchemy.url
sqlalchemy.url = postgresql+asyncpg://postgres:postgres@localhost:5432/fastpg- Edit
app/migrations/env.pywith following
from logging.config import fileConfig
from sqlalchemy import pool
from sqlalchemy.ext.asyncio import async_engine_from_config
from alembic import context
from models import Base
from geoalchemy2.admin.dialects.common import _check_spatial_type
from geoalchemy2 import Geometry, Geography, Raster
# this is the Alembic Config object, which provides
# access to the values within the .ini file in use.
config = context.config
# Interpret the config file for Python logging.
# This line sets up loggers basically.
fileConfig(config.config_file_name)
target_metadata = Base.metadata
# other values from the config, defined by the needs of env.py,
# can be acquired:
# my_important_option = config.get_main_option("my_important_option")
# ... etc.
def render_item(obj_type, obj, autogen_context):
"""Apply custom rendering for selected items."""
if obj_type == 'type' and isinstance(obj, (Geometry, Geography, Raster)):
import_name = obj.__class__.__name__
autogen_context.imports.add(f"from geoalchemy2 import {import_name}")
return "%r" % obj
# default rendering for other objects
return False
def include_object(object, name, type_, reflected, compare_to):
# Stop making 'index' for geometry column
if type_ == "index":
if len(object.expressions) == 1:
try:
col = object.expressions[0]
if (
_check_spatial_type(col.type, (Geometry, Geography, Raster))
and col.type.spatial_index
):
return False
except AttributeError:
pass
# Exclude 'spatial_ref_sys' from migrations
if type_ == "table" and name == "spatial_ref_sys":
return False
return True
def run_migrations_offline() -> None:
"""Run migrations in 'offline' mode.
This configures the context with just a URL
and not an Engine, though an Engine is acceptable
here as well. By skipping the Engine creation
we don't even need a DBAPI to be available.
Calls to context.execute() here emit the given string to the
script output.
"""
url = config.get_main_option("sqlalchemy.url")
context.configure(
url=url,
target_metadata=target_metadata,
literal_binds=True,
render_item=render_item,
include_object=include_object,
dialect_opts={"paramstyle": "named"},
)
with context.begin_transaction():
context.run_migrations()
def do_run_migrations(connection):
"""
This function is used to execute migrations within an async context.
"""
context.configure(connection=connection,
target_metadata=target_metadata,
render_item=render_item,
include_object=include_object,)
with context.begin_transaction():
context.run_migrations()
async def run_migrations_online() -> None:
"""Run migrations in 'online' mode.
In this scenario we need to create an Engine
and associate a connection with the context.
"""
connectable = async_engine_from_config(
config.get_section(config.config_ini_section),
prefix="sqlalchemy.",
poolclass=pool.NullPool,
)
async with connectable.connect() as connection:
await connection.run_sync(do_run_migrations)
if context.is_offline_mode():
run_migrations_offline()
else:
import asyncio
asyncio.run(run_migrations_online())- Edit
app/migrations/script.py.mako
"""${message}
Revision ID: ${up_revision}
Revises: ${down_revision | comma,n}
Create Date: ${create_date}
"""
from typing import Sequence, Union
from alembic import op
import sqlalchemy as sa
import geoalchemy2 # add geoalchemy to the migration file
${imports if imports else ""}
# revision identifiers, used by Alembic.
revision: str = ${repr(up_revision)}
down_revision: Union[str, None] = ${repr(down_revision)}
branch_labels: Union[str, Sequence[str], None] = ${repr(branch_labels)}
depends_on: Union[str, Sequence[str], None] = ${repr(depends_on)}
def upgrade() -> None:
${upgrades if upgrades else "pass"}
def downgrade() -> None:
${downgrades if downgrades else "pass"}- Generate migration automatically and upgrade head
alembic revision --autogenerate -m "init"
alembic upgrade head- Check your database to confirm if
alembic_versionandItemtables are added

Try creating one more model, and subsequent schema. Once done, generate migrations
Create APIs
We’ll start by creating CRUD functions and APIs
- Install packages
pip install "geoalchemy2[shapely]"- Create
crud.py
from sqlalchemy.ext.asyncio import AsyncSession
from sqlalchemy.future import select
from models import Item
from schemas import ItemCreate
from geoalchemy2 import WKTElement
from geoalchemy2.shape import to_shape
async def create_item(db: AsyncSession, item: ItemCreate):
db_item = Item(name=item.name, description=item.description, geom=WKTElement(item.geom, srid=4326) )
db.add(db_item)
await db.commit()
await db.refresh(db_item)
return {"status": 201,"message":'Added successfully'}
async def get_items(db: AsyncSession):
result = await db.execute(select(Item))
items = result.scalars().all()
for obj in items:
if isinstance(obj.geom, str):
obj.geom = WKTElement(obj.geom)
obj.geom = to_shape(obj.geom).wkt
return items- Create
routers/items.py
from fastapi import APIRouter, Depends
from sqlalchemy.ext.asyncio import AsyncSession
from database import get_db
from schemas import Item, ItemCreate
from crud import create_item, get_items
router = APIRouter()
@router.post("/")
async def create_new_item(item: ItemCreate, db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_db)):
res = await create_item(db, item)
return res
@router.get("/")
async def read_items(db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_db)):
return await get_items(db)- Update
main.py
from fastapi import FastAPI
from contextlib import asynccontextmanager
from routers import items # add router
from database import engine, Base
@asynccontextmanager
async def lifespan(app: FastAPI):
async with engine.begin() as conn:
await conn.run_sync(Base.metadata.create_all)
yield
app = FastAPI(lifespan=lifespan)
app.include_router(items.router, prefix="/items", tags=["items"]) # include router
@app.get("/")
def read_root():
return {"Hello": "World"}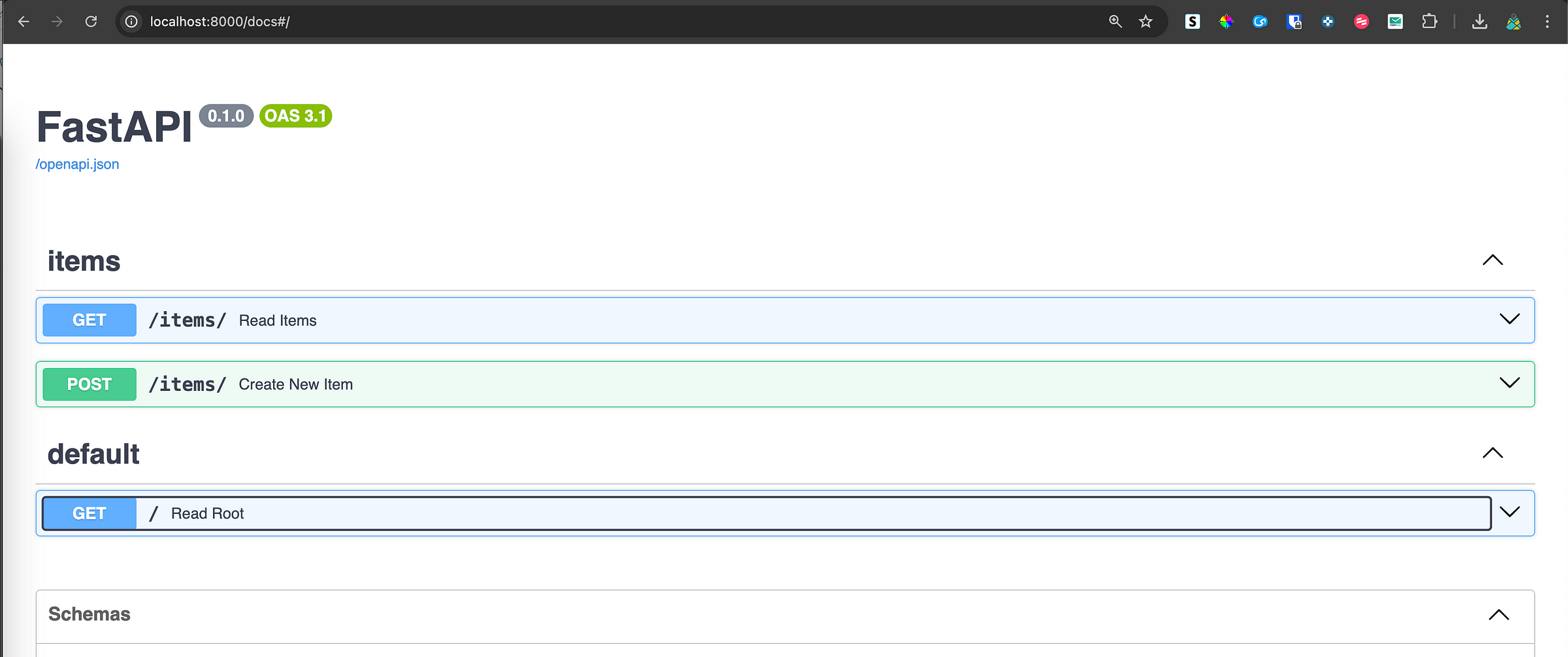
Try APIs
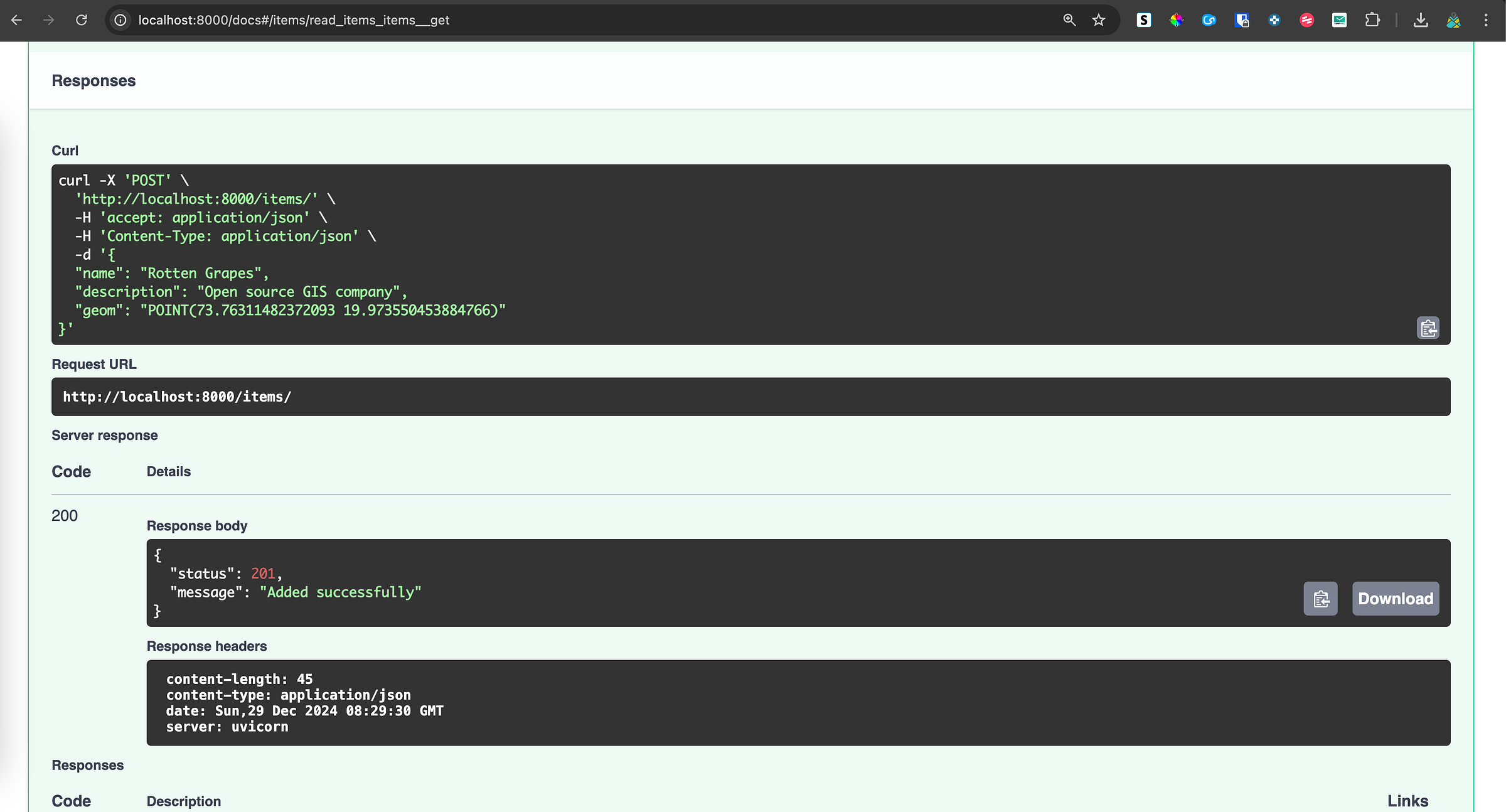
- Try sending body with WKT geometry to
POSTrequest
curl -X 'POST' \
'http://localhost:8000/items/' \
-H 'accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"name": "Rotten Grapes",
"description": "Open source GIS company",
"geom": "POINT(73.76311482372093 19.973550453884766)"
}'
GETall Items
curl -X 'GET' \
'http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/' \
-H 'accept: application/json'